Unlock Your Crypto Journey: An Amazing Guide to Crypto Wallet Basics ✨
Welcome to the exciting world of cryptocurrency! Whether you’re curious about Bitcoin, intrigued by Ethereum, or exploring the vast universe of digital assets, one thing is fundamental: understanding crypto wallet basics. Think of a crypto wallet as your personal gateway to the blockchain – the digital equivalent of your physical wallet, but for your digital money.
But it’s more than just storage; it’s about control, security, and interacting with the burgeoning world of Web3. This guide is designed for beginners, breaking down everything you need to know about cryptocurrency storage in a natural, engaging way. Forget dense textbooks; let’s embark on this learning journey together! We’ll cover the essentials, sprinkle in the latest trends, and ensure you feel confident managing your digital assets securely. Mastering crypto wallet basics is the crucial first step.
Why Crypto Wallets Matter More Than Ever 🤔
In the realm of cryptocurrency, you often hear the phrase “Not your keys, not your coins.” This highlights the core importance of crypto wallets. Unlike traditional banking where a third party holds your funds, crypto wallets empower you with true ownership and control over your digital assets.
Here’s why they are indispensable:
- Security Fortress: Crypto wallets are designed with security at their core. Using advanced encryption and unique keys (we’ll dive into these later!), they aim to ensure only you can access and manage your funds. In a decentralized world without central protectors, this personal security is paramount.
- You’re the Bank: Forget asking permission. With your own crypto wallet, you have full autonomy. You can send, receive, and manage your funds 24/7, anywhere in the world, without needing approval from any intermediary. This is financial self-sovereignty.
- Gateway to Web3: Modern wallets are evolving beyond simple storage. They are your interface to decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and even the Metaverse. They act as your digital identity and passport to the next generation of the internet.
- Accessibility for All: Anyone with an internet connection can set up a crypto wallet, promoting financial inclusion and empowering individuals globally to participate in the digital economy.
- Privacy Considerations: While blockchain transactions are transparent, wallets themselves don’t inherently require linking your real-world identity to your address (though regulations are evolving). This offers a degree of pseudonymity valued by many users.
- Managing Diversity: As you explore different cryptocurrencies, wallets allow you to hold and manage various assets in one place, simplifying portfolio oversight.
The world of digital assets is constantly innovating, and crypto wallets are at the forefront, incorporating features like enhanced biometric security, AI-driven insights, and seamless cross-chain interactions. Understanding and using them correctly is fundamental to safely navigating this space.
Unpacking the Types of Crypto Wallets 🪙
Not all wallets are created equal. They come in various forms, primarily differing in how they store your all-important private keys and balancing security with convenience. Let’s break down the main types of crypto wallets:
1. Software Wallets (Hot Wallets)
These are applications or programs installed on your computer or smartphone, or accessed via a web browser extension. They are called “hot wallets” because they are connected to the internet, offering convenience for frequent transactions but requiring robust security practices.
- Desktop Wallets: Installed directly onto your laptop or PC (e.g., Exodus). They offer a good balance of security (if your computer is secure) and functionality. You have more control over keys compared to web wallets.
- Pros: User-friendly interfaces, often support many cryptocurrencies, good features.
- Cons: Vulnerable if your computer gets malware; relies on your computer’s security.
- Mobile Wallets: Apps downloaded onto your smartphone (e.g., Trust Wallet, Exodus, MetaMask Mobile). Super convenient for on-the-go transactions and interacting with dApps via QR codes or built-in browsers.
- Pros: Portable, convenient, often feature-rich (dApp browser, staking).
- Cons: Risk if your phone is lost, stolen, or compromised; security depends on your phone’s security measures.
- Web/Browser Extension Wallets: Accessed through your internet browser, often as extensions (e.g., MetaMask). Extremely popular for interacting with DeFi and NFTs directly from your browser.
- Pros: Seamless dApp/DeFi integration, very convenient for web-based activities.
- Cons: Considered the least secure type of hot wallet due to constant internet exposure; risk of phishing attacks targeting extensions.
2. Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets)
These are physical devices, often resembling USB drives, that store your private keys completely offline. This is known as “cold storage.” Transactions are signed on the device itself, meaning your keys never touch the internet-connected computer or phone.
- Examples: Ledger (like the Nano S Plus or Stax), Trezor (like the Safe 3 or Safe 5).
- Pros: Highest level of security for storing significant amounts of crypto; immune to online hacking attempts targeting keys.
- Cons: Cost money to purchase; less convenient for quick, frequent transactions; risk of physical loss or damage (though recovery is possible with the seed phrase).
3. Paper Wallets (Cold Wallets)
This involves printing your public and private keys (often as QR codes) onto a physical piece of paper. It’s a form of deep cold storage.
- Pros: Completely offline, immune to digital threats.
- Cons: Highly susceptible to physical damage (fire, water), fading, or loss; cumbersome to use for transactions; generally considered outdated and less practical than hardware wallets for most users.
Choosing the Right Type:
- For everyday transactions and small amounts: Mobile or web wallets offer convenience.
- For significant holdings or long-term storage (“HODLing”): Hardware wallets are highly recommended for their superior security.
- Beginners often start with: A reputable software wallet (mobile or desktop) like Exodus or Trust Wallet for ease of use, potentially combined with a hardware wallet like Ledger or Trezor later for larger amounts.
- For heavy DeFi/NFT users: Browser extension wallets like MetaMask are essential, but should ideally be used cautiously, perhaps not for holding the bulk of your assets long-term.
Setting Up Your First Crypto Wallet (Software Focus) 🛠️
Ready to take the plunge? Setting up a software wallet is usually straightforward. Let’s walk through the typical steps, remembering that securing it from the start is crucial. We’ll use a generic process applicable to most reputable mobile or desktop wallets like Exodus or Trust Wallet.
- Choose Wisely: Select a well-regarded wallet that supports the cryptocurrencies you’re interested in. Prioritize wallets with strong security features, a good reputation, active development, and positive user reviews. Check their official website (like exodus.com or trustwallet.com) – avoid downloading from unofficial sources to prevent scams!
- Download & Install: Get the official app from the Google Play Store, Apple App Store, or the official desktop download link from the provider’s website (exodus.com, metamask.io). Install it on your device.
- Create a New Wallet: Launch the app. You’ll typically see options like “Create a New Wallet” or “Import Existing Wallet.” Choose “Create a New Wallet.”
- Set a Strong Password/PIN: The wallet will prompt you to create a password (desktop) or PIN (mobile). Use a strong, unique password/PIN that you don’t use elsewhere. This password encrypts your wallet file on your device but is not the master key to your funds (that’s next!).
- ⚠️ THE MOST IMPORTANT STEP: Backup Your Seed Phrase! ⚠️ This is non-negotiable. The wallet will generate a “Seed Phrase” (also called Recovery Phrase or Mnemonic Phrase) – usually 12 or 24 random words. This phrase is the master key to all your cryptocurrency associated with that wallet.
- Write it down: Physically write the words exactly in the correct order on paper.
- Store it securely OFFLINE: Keep this paper safe from fire, water, theft, and prying eyes. Think fireproof safe, safety deposit box (consider risks), or other highly secure, private locations. Store multiple copies in different secure locations if possible.
- NEVER store it digitally: Do not save it on your computer, phone notes, email, cloud storage, or take a photo of it. Digital storage makes it vulnerable to hackers.
- NEVER share it: No legitimate support team or service will ever ask for your seed phrase. Anyone asking is trying to scam you.
- Verification: The wallet app will likely ask you to re-enter the words in order to confirm you’ve backed them up correctly. Do this carefully.
- Understanding: If you lose your device and your seed phrase, your crypto is gone forever. If you lose your device but have your seed phrase, you can restore your wallet and funds on a new device. Your seed phrase IS your crypto.
- Explore & Secure: Familiarize yourself with the wallet’s interface. Find your receiving addresses, sending functions, and crucially, security settings. Enable options like Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) if offered, and explore biometric login (fingerprint/face ID) on mobile for added convenience and layer of security.
Congratulations! You’ve set up your first software wallet. Remember, security is an ongoing process.
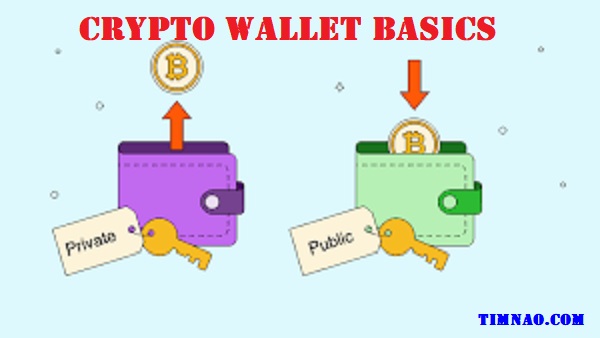
The Heart of Your Wallet: Public vs. Private Keys Explained 🔑
Understanding keys is fundamental to grasping crypto wallet basics. Your wallet doesn’t actually store your crypto like coins in a physical pouch. Instead, it manages cryptographic keys that prove your ownership of assets recorded on the blockchain.
- Public Key: Think of this like your bank account number. It’s derived from your private key and used to generate receiving addresses. You can safely share your public address (a specific format derived from the public key) with others so they can send you cryptocurrency. It lets people deposit funds into your account.
- Private Key: This is the crucial secret. Think of it like the password and signature authority for your bank account, all rolled into one. It’s a long string of characters that grants complete control over the cryptocurrency associated with its corresponding public key/address. Whoever has the private key owns the crypto. This is what your wallet secures, and what your seed phrase allows you to regenerate. Never share your private key.
- Wallet Address: This is a specific alphanumeric string derived from your public key, tailored for receiving a particular cryptocurrency (e.g., a Bitcoin address looks different from an Ethereum address). You generate these within your wallet to receive funds.
How it Works: When someone sends crypto to your public address, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, essentially saying “This amount now belongs to the address associated with this public key.” To spend or send that crypto later, you use your wallet software, which accesses your private key (securely stored within the wallet environment) to create a digital signature. This signature proves to the network that you authorize the transaction from your address. Without the correct private key, the transaction cannot be signed, and the funds cannot be moved.
This public/private key system is the foundation of cryptocurrency storage security and user control. Your wallet’s main job is to keep that private key safe while making it usable for you to manage your assets.
Sending & Receiving Crypto Like a Pro 💸
Now that you have a wallet and understand keys, let’s look at the practical side: moving crypto.
Receiving Cryptocurrency:
- Find Your Receiving Address: Open your wallet and select the specific cryptocurrency you want to receive (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). Look for an option like “Receive,” “Deposit,” or similar.
- Get the Address: Your wallet will display your unique receiving address for that specific coin. It will be a long string of letters and numbers, often accompanied by a QR code.
- Share the Address: Carefully copy this address (use the copy button!) or let the sender scan the QR code. Double-check you’re sharing the address for the correct cryptocurrency on the correct network (e.g., sending Ethereum to a Bitcoin address will result in lost funds).
- Wait for Confirmation: Once the sender initiates the transaction, it needs to be confirmed by the blockchain network. This can take anywhere from a few seconds to minutes or longer, depending on the network congestion and the transaction fee paid. Your wallet will usually show the transaction as “pending” and then “confirmed” or “completed” once it has received enough network confirmations. The funds will then reflect in your balance.
Sending Cryptocurrency:
- Initiate Sending: Open your wallet, select the crypto you want to send, and find the “Send” or “Transfer” option.
- Enter Recipient’s Address: Crucially, carefully paste the recipient’s correct wallet address. Double-check, even triple-check it. Sending to the wrong address is almost always irreversible. Avoid manual typing if possible; use copy-paste. Verify the first and last few characters.
- Enter the Amount: Specify how much crypto you want to send. You might be able to enter the amount in crypto (e.g., 0.01 BTC) or its equivalent fiat value (e.g., $500 worth of BTC).
- Check Network Fees: Cryptocurrency transactions require a network fee (or “gas fee” on networks like Ethereum) paid to the network validators/miners who process your transaction. Your wallet will usually estimate this fee. Higher fees generally mean faster confirmation times, especially during network congestion. Some wallets allow you to adjust the fee (be cautious; too low a fee can cause transactions to get stuck).
- Review and Confirm: Before hitting send, meticulously review all details: the recipient’s address, the amount, and the network fee. Most wallets have a final confirmation step.
- Send! Once confirmed, your wallet signs the transaction with your private key and broadcasts it to the network.
- Track (Optional): You can usually track the transaction’s progress on a blockchain explorer using the Transaction ID (TxID) provided by your wallet.
The Golden Rule: ALWAYS DOUBLE-CHECK ADDRESSES! Sending crypto is like sending cash in a digital envelope – once it’s gone to the wrong place, it’s incredibly difficult, usually impossible, to get back.
Fort Knox Security for Your Digital Assets 🛡️
In the world of crypto, you are responsible for your security. Unlike a bank that might refund fraudulent charges, if your crypto wallet is compromised due to negligence, your funds can be permanently lost. Prioritizing security isn’t optional; it’s essential. Here are best practices:
- Strong Passwords/PINs: Use complex, unique passwords/PINs for your wallet applications. Don’t reuse passwords from other accounts. Consider using a password manager.
- Seed Phrase Sanctity: As emphasized before: back up your seed phrase offline, store it securely in multiple locations if possible, and never share it or store it digitally. This is your ultimate recovery tool and the keys to your kingdom.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If your wallet or associated exchange accounts offer 2FA (using an app like Google Authenticator or Authy, or a hardware key like YubiKey), enable it. This adds a critical layer of security beyond just a password. SMS-based 2FA is better than nothing but generally considered less secure.
- Leverage Biometrics: Use fingerprint or facial recognition on mobile wallets if available. It adds convenience and another security hurdle for unauthorized physical access to your device.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your wallet software (desktop/mobile app/extension) and your device’s operating system. Updates often contain crucial security patches that fix vulnerabilities exploited by hackers.
- Beware of Phishing & Scams: This is HUGE. Scammers are constantly devising new tricks:
- Fake Wallet Apps/Updates: Only download/update wallets from official app stores or the official website. Be wary of lookalike apps.
- Fake Support: Legitimate support will NEVER ask for your seed phrase or private keys, nor ask you to send crypto to “verify” your wallet. Be extremely suspicious of unsolicited DMs or emails offering help.
- Phishing Websites: Scammers create fake login pages for wallets or exchanges. Always double-check the website URL before entering credentials. Bookmark official sites. Never click suspicious links in emails or messages.
- Malicious Airdrops/NFTs: Be wary of unexpected free tokens or NFTs appearing in your wallet. Interacting with malicious smart contracts (e.g., trying to sell or move them) can sometimes drain your wallet. Research before interacting. Some wallets (like Trust Wallet) are introducing security scanners to flag risky transactions or contracts.
- Social Engineering: Scammers might impersonate friends, influencers, or project teams to trick you into sending funds or revealing sensitive information. Verify requests through separate channels.
- Secure Your Device & Network: Keep your computer and smartphone free of malware using reputable antivirus software. Avoid using public Wi-Fi for accessing your wallets or making transactions; use a trusted network or a VPN.
- Use Hardware Wallets for Significant Amounts: For long-term storage or large sums, move funds off hot wallets and onto a hardware wallet (Ledger, Trezor).
- Start Small & Test: When sending to a new address, consider sending a small test amount first to ensure it arrives correctly before sending a larger sum.
- Regularly Monitor Accounts: Keep an eye on your transaction history for any unauthorized activity.
Security is about layers and vigilance. Staying informed about common scams and following these practices dramatically reduces your risk.
Advanced Security: Cold Storage & Multisig Wallets 🥶✍️
For users needing even higher levels of security, especially businesses or individuals managing substantial assets, two advanced concepts are key:
Cold Storage
As mentioned earlier, cold storage simply means keeping your private keys completely offline, away from internet connections. This makes them immune to online hacking, malware, and phishing attacks that target keys stored on connected devices.
- Methods: The most common and practical methods are:
- Hardware Wallets: (Ledger, Trezor) Physical devices purpose-built for secure offline key storage and transaction signing. They are the gold standard for most serious users.
- Paper Wallets: Printing keys on paper. Secure if the paper is protected, but impractical and risky due to physical vulnerability.
- Air-gapped Computers: Using a computer that has never been and will never be connected to the internet to generate and store keys (highly technical).
- Best For: Long-term holding (“HODLing”) of significant cryptocurrency value. It prioritizes security over convenience.
Multisignature (Multisig) Wallets
Imagine needing multiple keys to open a bank vault. That’s the idea behind multisig wallets. They require signatures from multiple private keys before a transaction can be broadcast.
- How it Works: A multisig wallet is configured with a specific setup, like “2-of-3” or “3-of-5.”
- A 2-of-3 setup means three private keys are associated with the wallet, but any two of those keys are needed to approve a transaction.
- A 3-of-5 setup requires signatures from three out of the five associated keys.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: If one key is compromised or lost, the funds remain secure because the attacker/loser doesn’t have the required number of keys.
- Redundancy: If one keyholder loses their key, others can still authorize transactions.
- Shared Control: Ideal for businesses or groups where multiple parties need to approve expenditures, preventing unilateral actions.
- Use Cases: Company treasuries, joint accounts, escrow services, enhanced personal security (e.g., keeping keys on different devices/locations).
- Implementation: Can be set up using specialized wallet software or platforms that support multisig functionality. Some hardware wallets also support multisig setups.
Both cold storage and multisig wallets add layers of security, trading some convenience for significantly enhanced protection against various threats.
Managing a Diverse Crypto Portfolio in One Wallet 💼
As you delve deeper, you might acquire different cryptocurrencies. Managing them efficiently becomes important.
- Choose a Multi-Currency Wallet: Select a wallet known for supporting a wide range of coins and tokens (often called altcoins). Wallets like Exodus, Trust Wallet, or hardware wallets (Ledger, Trezor combined with their software like Ledger Live or Trezor Suite) are designed for this.
- Organization is Key:
- Separate Addresses: Use the distinct receiving addresses your wallet generates for each specific crypto. Don’t send Bitcoin to an Ethereum address!
- Labeling/Tagging: Some wallets allow you to label addresses or transactions, which can help organize funds for different purposes (e.g., “Long-term Hold,” “Trading Funds”).
- Portfolio Trackers: While some wallets offer basic portfolio views, dedicated portfolio tracking apps or websites can provide a more comprehensive overview. These tools often connect via API (read-only access, ensure security) or require manual entry to:
- Monitor total portfolio value in real-time.
- Track performance of individual assets.
- View historical data and charts.
- Help with tax reporting by consolidating transaction history.
- Examples include CoinStats, Delta, Blockfolio (now FTX). Always research the security and privacy implications before connecting your wallets or exchanges.
- Diversification Strategy: Holding multiple cryptocurrencies can be a risk management strategy. Diversification means spreading investments across different assets to potentially reduce the impact if one performs poorly. Research different projects, understand their use cases and risks, and allocate funds according to your investment goals and risk tolerance. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket!
A good multi-currency wallet combined with organizational discipline (and potentially a tracker) makes managing a diverse crypto portfolio much easier.
The Evolving Wallet: Web3, DeFi, NFTs, and Beyond 🚀
Modern crypto wallets are rapidly evolving beyond simple cryptocurrency storage. They are becoming dynamic hubs for interacting with the decentralized web (Web3). Here are some key trends and features shaping the future:
- Seamless DeFi Integration: Many wallets (MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Exodus) now feature built-in dApp browsers or direct connection capabilities (like WalletConnect). This allows users to easily interact with DeFi protocols for:
- Swapping/Trading: Exchanging tokens directly via decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
- Staking: Locking up crypto to support a network and earn rewards.
- Lending & Borrowing: Participating in decentralized money markets.
- Yield Farming: Providing liquidity to DEXs to earn fees and rewards.
- NFT Management: As NFTs gained popularity, wallets adapted. Many now allow users to:
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: A major trend is improving the ability to manage and move assets across different blockchain networks seamlessly within one wallet, reducing the need for complex bridges or multiple wallets.
- AI-Powered Features: Emerging wallets are integrating Artificial Intelligence for:
- Personalized financial insights and analytics.
- Predictive market alerts.
- Automated portfolio management or rebalancing suggestions.
- Enhanced security through behavioral biometric analysis.
- Decentralized Identity (DID): Wallets are evolving into secure containers for managing verifiable digital identities and credentials (like IDs, certificates, records) – putting users in control of their personal data.
- Metaverse & Web3 Integration: Wallets are becoming the key to accessing and interacting within Metaverse platforms and other Web3 ecosystems – managing virtual land, in-game assets, digital avatars, and facilitating transactions within these virtual worlds.
- Enhanced Security Innovations: Beyond 2FA, we’re seeing advancements like:
- More sophisticated biometric security (facial, voice, behavioral).
- Built-in security scanners (like Trust Wallet’s) to flag risky transactions or dApps.
- Potential integration of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) for key management, offering alternatives to traditional seed phrases for some users.
- Sustainability Focus: Some wallets are adding features to track the carbon footprint of transactions or incentivizing interaction with eco-friendly blockchains (Proof-of-Stake networks).
Your crypto wallet is increasingly becoming your central command center for navigating the expanding digital frontier.
Troubleshooting Common Wallet Woes 🤔
Even with the best wallets, you might occasionally encounter hiccups. Here’s how to address some common issues:
- Forgotten Password/PIN:
- Problem: You can’t access the wallet application on your device.
- Solution: This password/PIN usually only locks the app on that specific device. Your funds are tied to your seed phrase, not this app password. If you forget the password/PIN, you’ll likely need to uninstall and reinstall the wallet app (or install it on a new device) and then use your seed phrase to restore access to your funds. Check the wallet provider’s support documentation for the exact recovery process. This underscores why securing your seed phrase is paramount.
- Lost Seed Phrase:
- Problem: You’ve lost the paper(s) where you wrote down your 12/24-word recovery phrase.
- Solution: This is critical. If you still have access to your wallet on your device, immediately try to find a way within the wallet settings to view or back up your seed phrase again. If the wallet doesn’t allow this, create a new wallet, back up its seed phrase securely, and then transfer all your funds from the old (compromised backup) wallet to the new, securely backed-up wallet. If you lose access to your device and have lost your seed phrase, your funds are likely irretrievably lost. There is no central authority to help you recover them.
- Transaction Delayed or Stuck:
- Problem: You sent crypto, but it’s taking a very long time to confirm, or it seems stuck as “pending.”
- Solution: This is often due to network congestion or setting the transaction fee too low. Check a blockchain explorer for the network’s status. Some wallets allow you to “speed up” a transaction by paying a higher fee (this essentially replaces the old transaction with a new one with a better incentive for miners/validators). Check your wallet’s documentation for options.
- Sent to Wrong Address/Network:
- Problem: You accidentally pasted the wrong recipient address or sent a coin on the wrong blockchain network (e.g., sending ETH via the BSC network instead of the Ethereum network).
- Solution: Unfortunately, blockchain transactions are typically irreversible. If you sent to a completely invalid address, the funds might be lost forever. If you sent to someone else’s valid address by mistake, you can only hope they are honest enough to return it (but there’s no obligation). If you sent on the wrong network but to an address you control on that other network, there might be complex ways to recover it, often requiring technical expertise and specific wallet support – research carefully or seek expert help cautiously (beware recovery scams!). Prevention (double-checking addresses) is the best cure.
- Wallet Not Syncing / Incorrect Balance:
- Problem: Your wallet isn’t showing the latest transactions or the correct balance.
- Solution: Ensure you have a stable internet connection. Make sure your wallet software is updated to the latest version. Try refreshing the wallet or restarting the application. Sometimes, network congestion can cause display delays. If the issue persists, check the wallet provider’s support channels or community forums – there might be a known temporary issue. You can always verify your true balance by checking your public address on a reliable blockchain explorer.
- Suspected Security Breach:
- Problem: You notice unauthorized transactions, or suspect your device/keys might be compromised.
- Solution: Act immediately. If possible, quickly transfer any remaining funds to a new, secure wallet (preferably a hardware wallet or a software wallet on a known-clean device) whose seed phrase has never been exposed digitally. Disconnect the compromised wallet from the internet. Report the incident if relevant (e.g., to an exchange if an linked account was breached). Change passwords on related accounts. Analyze how the breach might have happened (malware, phishing?) to prevent recurrence.
When troubleshooting, always refer to the official support documentation of your specific wallet provider first, and be extremely wary of unsolicited help offers online, especially those asking for sensitive information.
Staying Sharp: Keeping Up with Wallet Tech 📰
The crypto wallet landscape changes rapidly. New features emerge, security threats evolve, and new projects launch constantly. Staying informed is crucial for managing your assets safely and effectively.
- Follow Reputable Sources: Keep up with trusted crypto news websites (CoinDesk, Cointelegraph, Decrypt), blogs from wallet providers (Ledger, Trezor, Exodus, Trust Wallet), and respected industry analysts on social media (Twitter/X, YouTube).
- Update Your Software: As mentioned, regularly update your wallet apps and device OS for security and new features. Read the release notes to understand what’s changed.
- Engage with Communities: Participate (or lurk!) in online forums (like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency) or Discord/Telegram groups related to your wallet or favorite projects. You can learn from others’ experiences and ask questions (but always verify information and beware of scammers).
- Understand Security Trends: Pay attention to reports about new scams or vulnerabilities. Forewarned is forearmed.
- Continuous Learning: Don’t stop at the basics. Explore concepts like different blockchain consensus mechanisms, smart contracts, DeFi protocols, and NFT standards. The more you understand the underlying tech, the better equipped you’ll be. Attend webinars or online courses if you’re keen to deepen your knowledge.
The world of crypto wallets is dynamic. Embracing ongoing learning is key to navigating it successfully.
Conclusion: Your Crypto Journey Starts Securely – 10 Amazing Things to Remember! 🏁
We’ve journeyed through the essentials of crypto wallet basics, equipping you with the foundational knowledge to navigate the world of digital assets. From the ‘why’ and ‘what’ to the ‘how-to’ of securing and using your wallet, understanding these concepts is key.
To truly master the crypto wallet basics and ensure secure crypto wallet practices, here are 10 amazing things every beginner must know and remember:
- You Hold the Power (and Responsibility): Crypto wallets give you direct ownership and control over your assets – unlike traditional banks. This means you are solely responsible for their security. Remember: “Not your keys, not your coins.”
- Keys Unlock Everything: Grasp the difference between your shareable public address (for receiving funds) and your critical private key (for sending/controlling funds). Never share your private key.
- Your Seed Phrase is GOLD: The 12/24-word recovery phrase is the master key to your wallet. Secure it OFFLINE, never store it digitally, and never share it. Losing it means losing your crypto if your device fails.
- Choose the Right Tool for the Job: Understand the different types of crypto wallets. Hot wallets (software: mobile/desktop/web) offer convenience for small amounts/frequent use, while Cold wallets (hardware) provide maximum security for larger amounts/long-term holds.
- Security is Non-Negotiable: Implement layers of security: strong unique passwords/PINs, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) wherever possible, and keep your wallet software and device OS updated.
- Scam Artists Are Everywhere: Be hyper-vigilant! Watch out for phishing links, fake websites/apps, fake support staff asking for keys/phrases, and suspicious airdrops. Verify everything.
- Measure Twice, Send Once: Always meticulously double-check recipient addresses before sending cryptocurrency. Transactions are irreversible; mistakes can be costly and permanent.
- Hardware Wallets = Fort Knox: For significant amounts of cryptocurrency you plan to hold long-term, investing in a reputable hardware wallet (Ledger, Trezor) is the safest cryptocurrency storage method.
- Wallets Are Your Web3 Passport: Modern wallets do more than store crypto; they are your gateway to interacting with Decentralized Finance (DeFi), NFTs, dApps, and the evolving Metaverse.
- Learning Never Stops: The crypto space evolves constantly. Stay curious, follow reputable sources, learn about new security threats, and continuously update your knowledge to stay safe and informed.
Mastering these 10 points provides a solid foundation. It might seem like a lot, but prioritizing security and understanding these core principles will allow you to explore the innovative world of cryptocurrency with much greater confidence.
Your adventure in tomorrow’s tech starts now. Explore wisely, stay secure, and enjoy the possibilities!
Reference video: